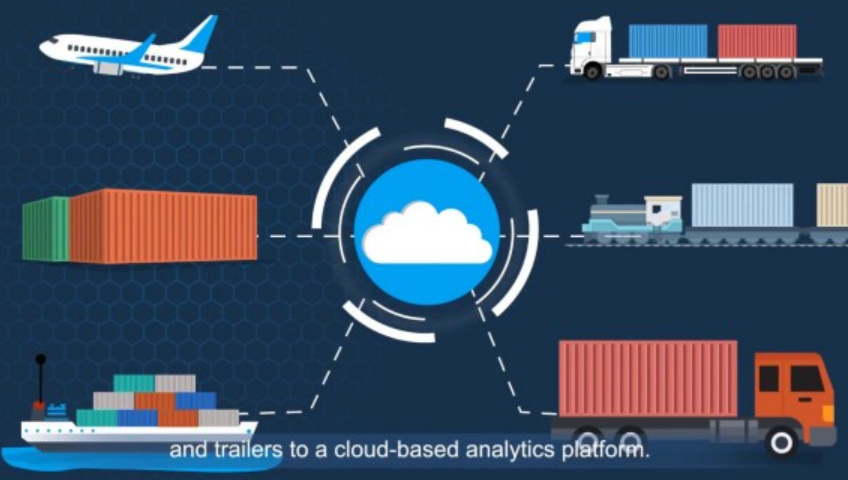
1. Introduction to Cargo Tracking
In today’s globalized world, cargo tracking plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth movement of goods across borders and oceans. At its core, cargo tracking refers to the process of monitoring the location and status of shipments from the point of origin to the final destination. This system provides real-time information, enabling businesses and consumers to know exactly where their goods are at any given moment. The importance of cargo tracking cannot be overstated, as it enhances the efficiency of supply chains, reduces losses, and ensures the timely delivery of products.
Cargo tracking has become an integral part of modern logistics, offering transparency and accountability in the movement of goods. Whether it’s a multinational corporation shipping goods overseas or an individual awaiting an online purchase, cargo tracking offers peace of mind by providing up-to-date information on the shipment’s progress.
2. History of Cargo Tracking Systems
The concept of tracking cargo has evolved significantly over the years. In the early days of trade, tracking was rudimentary at best, relying on physical records and manual updates. The introduction of the telegraph in the 19th century marked the first major advancement, allowing shipping companies to communicate the status of cargo over long distances.
The advent of barcodes and scanning technologies in the 20th century further revolutionized cargo tracking. These innovations allowed for automated tracking systems, reducing human error and increasing the accuracy of shipment information. As technology advanced, so did cargo tracking methods, with the introduction of GPS (Global Positioning System) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technologies enabling real-time tracking of shipments. These systems have become more sophisticated over time, incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) devices and satellite communication, which have made global tracking more reliable and precise.
3. How Cargo Tracking Works
Cargo tracking is a complex system that integrates various technologies to provide accurate and real-time information about a shipment’s location. At the core of most cargo tracking systems is GPS technology, which uses satellites to determine the exact position of a shipment. This data is then transmitted to tracking platforms, where it can be accessed by shippers, carriers, and customers.
RFID technology plays a critical role in cargo tracking, especially in warehouses and during the loading and unloading of goods. RFID tags attached to cargo items transmit data to receivers, allowing for automated inventory management and reducing the risk of lost or misplaced items.
In addition to GPS and RFID, the Internet and satellite communication are vital components of cargo tracking systems. These technologies allow for the seamless transmission of tracking data across the globe, ensuring that stakeholders have access to real-time updates regardless of the shipment’s location.
4. Types of Cargo Tracking Systems
Cargo tracking systems can be categorized into several types based on their functionality and the technology used. The most common types are:
- Active vs. Passive Tracking Systems: Active tracking systems continuously transmit data in real-time, providing constant updates on the shipment’s location. In contrast, passive tracking systems record data that can be accessed later, often when the shipment reaches its destination.
- Real-Time Tracking Systems: These systems use GPS and other technologies to provide live updates on the shipment’s location. Real-time tracking is crucial for high-value goods and time-sensitive deliveries.
- Batch Tracking Systems: These systems are used for tracking groups of items together, rather than individual items. This is common in industries where bulk shipments are standard, such as agriculture or raw materials.
5. Technologies Used in Cargo Tracking
Several technologies are essential for effective cargo tracking. GPS is perhaps the most well-known, providing precise location data via satellites. This technology is complemented by RFID systems, which are particularly useful for tracking items in close proximity, such as within a warehouse or during transportation.
Barcode systems remain a staple in cargo tracking, especially for inventory management. Barcodes are scanned at various checkpoints, providing a record of the shipment’s journey.
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has also impacted cargo tracking significantly. IoT devices, such as smart sensors, can monitor the condition of the cargo, such as temperature and humidity, in addition to its location. This is particularly valuable for industries like pharmaceuticals and food, where maintaining specific conditions is crucial.
6. Benefits of Cargo Tracking
The benefits of cargo tracking are vast and touch on several key aspects of the supply chain. Enhanced security and safety are among the top advantages, as tracking systems help prevent theft and loss by providing constant visibility of goods.
Improved operational efficiency is another significant benefit. With real-time data, companies can optimize routes, reduce delays, and make informed decisions that streamline their operations. Additionally, the availability of real-time data allows for better reporting and analytics, enabling businesses to identify trends and make data-driven decisions.
Cost savings are also a direct benefit of effective cargo tracking. By reducing losses, improving efficiency, and enabling better planning, companies can lower their overall logistics costs.
7. Challenges in Cargo Tracking
Despite its numerous benefits, cargo tracking faces several challenges. Security concerns are paramount, as the data transmitted by tracking systems can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of this data is crucial to maintaining trust in these systems.
Technical limitations and accuracy issues can also pose challenges. For example, GPS signals can be obstructed by physical barriers, leading to inaccurate location data. Furthermore, the high implementation costs of advanced tracking systems can be a barrier for smaller companies.
8. Cargo Tracking in Different Industries
Cargo tracking is utilized across various industries, each with unique requirements:
- Shipping and Freight: Cargo tracking ensures the timely and secure delivery of goods across long distances, often involving multiple modes of transportation.
- Aviation: In the aviation industry, tracking systems are used to monitor luggage and cargo, ensuring that items reach their destination efficiently and safely.
- E-commerce and Retail: With the rise of online shopping, cargo tracking has become essential in providing customers with real-time updates on their purchases.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: The tracking of temperature-sensitive goods, such as vaccines, is critical in the pharmaceutical industry, where maintaining specific conditions is crucial for product integrity.
9. Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Cargo tracking systems are subject to various legal and regulatory frameworks, particularly concerning international regulations. Compliance with these regulations is essential for companies operating across borders.
Data privacy concerns are also a significant consideration, as tracking systems collect and transmit large amounts of data. Ensuring compliance with local and international data protection laws is vital.
10. Future Trends in Cargo Tracking
The future of cargo tracking is set to be shaped by several emerging technologies. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role, enabling predictive analytics and more sophisticated tracking capabilities.
Blockchain technology is another trend that holds promise for the cargo tracking industry. Blockchain can provide a secure, immutable record of a shipment’s journey, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing transparency.
Predictive analytics and automation are also expected to grow in importance, allowing companies to anticipate delays and optimize routes in real-time.
11. Major Players in the Cargo Tracking Industry
Several companies lead the cargo tracking industry, offering advanced solutions to businesses worldwide. DHL, UPS, and FedEx are among the top logistics companies that have integrated sophisticated tracking systems into their operations.
In addition to these established players, startups are also making significant contributions to the industry. Companies like Traxens and SkyBitz are innovating with new technologies and approaches to cargo tracking.
12. Case Studies of Successful Cargo Tracking Implementation
Examining case studies can provide valuable insights into how cargo tracking systems are implemented effectively:
- Case Study 1: DHL – DHL’s use of IoT devices and advanced analytics has enhanced its cargo tracking capabilities, improving delivery times and reducing losses.
- Case Study 2: Amazon – Amazon’s extensive logistics network relies heavily on real-time tracking to manage its global operations, ensuring that millions of packages are delivered efficiently.
- Case Study 3: Maersk – Maersk, a leader in shipping, has implemented advanced tracking systems to monitor its fleet and cargo, optimizing routes and improving overall efficiency.
13. How to Choose the Right Cargo Tracking System
Choosing the right cargo tracking system depends on several factors. Assessing your needs is the first step, determining whether you require real-time tracking, batch tracking, or a combination of both.
Evaluating different solutions involves comparing the features and costs of various systems. It’s essential to conduct a cost vs. benefit analysis to ensure that the chosen system provides value for money.
14. Cargo Tracking Best Practices
Implementing a cargo tracking system requires adherence to best practices to ensure its effectiveness. Training and educating staff on how to use the system is crucial, as is regular system maintenance and upgrades to keep the technology current.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the most reliable cargo tracking system? The reliability of a cargo tracking system depends on the specific needs of the business, including the type of goods being shipped and the required level of visibility.
- How does real-time cargo tracking work? Real-time cargo tracking uses GPS and other technologies to provide constant updates on the shipment’s location, offering live data to stakeholders.
- What are the costs associated with cargo tracking? Costs vary depending on the system’s complexity and features, ranging from basic solutions to advanced systems with real-time tracking and analytics.
- How secure are cargo tracking systems? Security varies by system, but most modern cargo tracking systems include encryption and other security measures to protect data.
- Can cargo tracking be used for small packages? Yes, cargo tracking systems can be scaled to track small packages, often using simpler technologies like barcodes or RFID.
- What are the future trends in cargo tracking? Future trends include the integration of AI, blockchain technology, and predictive analytics to enhance tracking capabilities and provide more accurate data.
16. Conclusion
Cargo tracking is an essential component of modern logistics, offering numerous benefits, from enhanced security to improved efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of cargo tracking systems, making them even more integral to global trade. Businesses must stay informed of the latest trends and best practices to leverage cargo tracking effectively, ensuring that their supply chains remain competitive in an increasingly complex world.